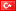
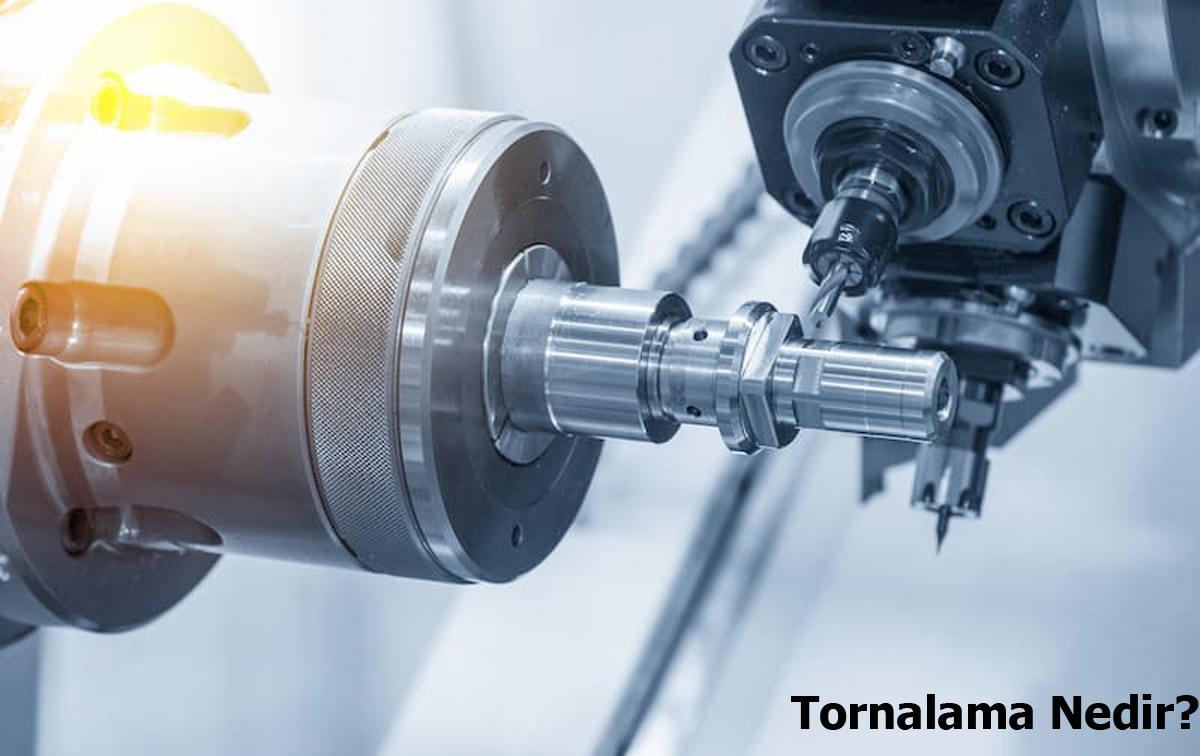
What is Turning?
Turning is one of the machining methods; covers a production process performed with CNC lathes. With the development of technology, turning and CNC lathes have developed. The production of many products that could not be produced technically and mechanically began to be made with CNC lathes. This enabled the turning method to be used more in industry.
Turning is a machining process used to cut the excess on a workpiece and shape it into the desired shape. The turning method is a branch of machining. Turning with the cutting tool on a linear plane; is done using a workpiece with a lathe or CNC lathe.
Turning is a unit operation common in manufacturing as a mass reduction step where the main movement of the single-end cutting tool is parallel to the axis of rotation of the rotating workpiece, thereby creating outer surfaces.
In machining, several operations take place in a planned sequence to achieve the best results. There are 3 commonly used methods, including turning, drilling, and milling. This process is a very common and versatile manufacturing process. Thus, it is possible to process various types of materials using these three methods. Metals, plastics, composites, and wood are the most commonly processed workpieces.
Turning involves the rotation of the workpiece while the cutting tool moves in a linear motion. This creates a cylindrical shape. The lathe is the machine of choice for all turning operations.
At Aktif Lazer, we are making machining using a CNC turning machine. You can also contact us to take advantage of this service.
What is the process of turning?
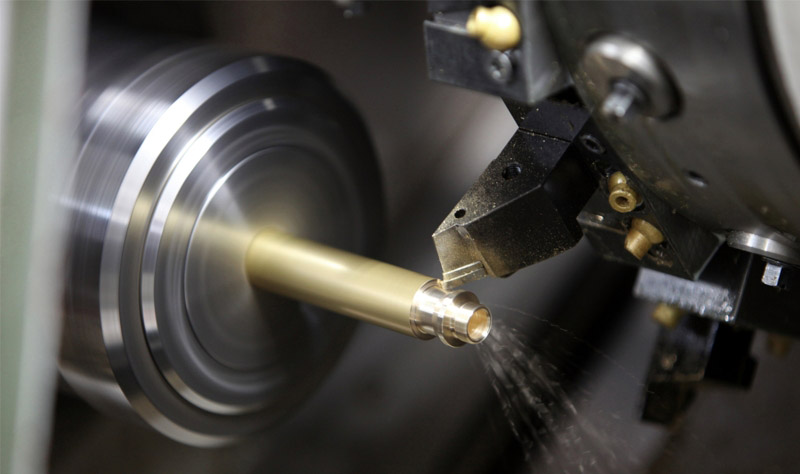

Like most machining operations, turning is done manually or automatically. The disadvantage of manual turning is that it requires constant supervision. No supervision is required in automatic turning. With the CNC, you can program all movements, speeds, and tool changes to a computer to automatically perform CNC turning. These instructions are sent to the lathe for execution. CNC turning ensures the consistency and efficiency of high-quality production runs.
Single point cutting tools used in turning come in a variety of shapes. They are placed at different angles for various results.
In turn, the cutting tool gradually creates a surface by removing chips from a workpiece that is rotated and fed to a cutting tool, and these chips are swept away by the rotation of the workpiece.
This turning is also commonly used as a secondary operation to add or improve features on parts manufactured using a different process.
What is turning used for?
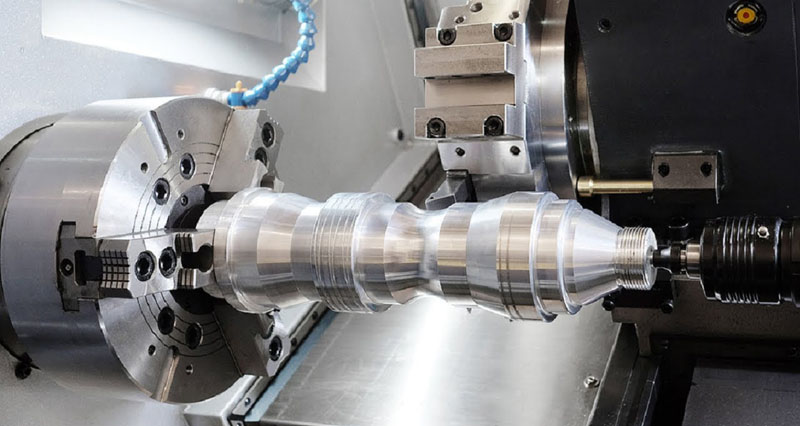

Turning; It is used to produce rotating, typically axisymmetric parts with many features such as holes, grooves, threads, tapers, surfaces of various diameters. Parts produced entirely by turning often include components used in limited quantities, such as specially designed shafts and fasteners, perhaps for prototypes. Turning is also commonly used as a secondary process to add features to parts manufactured using a different process. Due to the high tolerances and surface finish that turning can offer, its basic shape is ideal for adding precision turning features to a preformed part.
What are the Types of Turning?
Turning operations involve the process of shaping a workpiece with single-ended cutting tools. This is how turning types are determined. Before determining the turning type, it should be determined which process will be applied to the material. For example, it allows us to decide on the type of turning whether the material will be roughed or finished.
When it comes to turning types, 2 types of turning methods come to mind. These;
External Diameter Turning
External turning is a forming method performed along the outer diameter of the workpiece. In this method, which is carried out by machining the outer diameter of the material piece, face turning, longitudinal turning, and profile turning methods are used.
Face turning: In this method, the face of the workpiece is machined and is the method used to determine the actual length of the workpiece.
Longitudinal turning: This method is used to determine the diameter of the workpiece. The cut is made along the axis of the workpiece and the longitudinal turning with diameter reduction is performed.
Profile turning: In this method, the depth of the workpiece is determined and the machining speed is controlled.
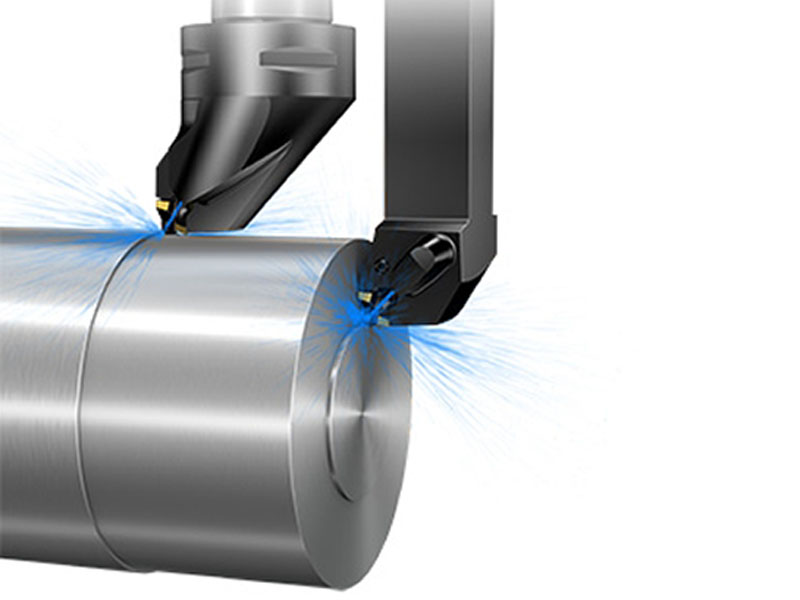
Internal Diameter Turning
Internal turning is a type of turning performed by drilling a piece of material. In this method, the inner diameter of the part is determined.
Taper turning: A method used to produce a tapered surface from a cylindrical workpiece by gradual reduction or diameter increase. This connecting process has a wide range of uses in the construction of machines. Almost all machine spindles have tapered holes on various tools.
Spherical turning: Spherical turning tools are used to create a ball shape on the workpiece.
Threading: Both standard and non-standard threads can be turned on a lathe using a suitable cutting tool. (Usually, it has a 60 or 55° nose angle)
Reaming: A sizing process that removes a small amount of metal from a pre-drilled hole. It is made to make internal holes of very precise diameters. For example, a 6 mm hole is drilled with a 5.98 mm drill bit and then reamed to the correct dimensions.
Slicing: Also called slicing or cutting, this process is used to create deep grooves that will remove a finished or partially finished component from the main stock.
Grooving: Grooving is the process of cutting a completed/partially completed workpiece to a certain depth. Grooving can be done on the inner and outer surfaces as well as on the face of the part (also known as face grooving or trepanning).
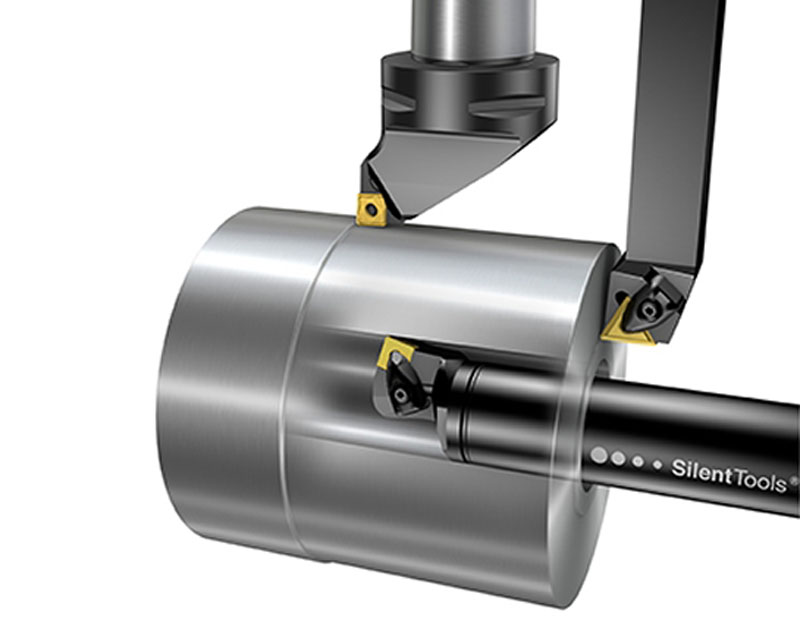

Where to use Turning?
Aerospace, automotive, medical, oil and gas, etc. These are some of the industries where CNC turning centers are used. These machines are especially suitable for round metal parts, rods, pipes, gears, etc. successful in processing.
If you are going to have turning operations, you can get detailed information about turning prices by contacting us.